BASIC PDU BUYING GUID
What is a Power Distribution Unit (PDU)?
A Power Distribution Unit (PDU) is a piece of equipment featuring numerous outlets intended for dispersing power to computers, servers, network switches, and other IT devices housed within a rack. PDUs are available in diverse configurations, offering a range of functionalities spanning from fundamental power distribution to advanced remote power administration.
How to select the appropriate power distribution unit (PDU) for an IT server rack or network closet.
This guide aims to assist you in:
1) Grasping the concept of a PDU and identifying its essential characteristics
2) Understanding the crucial inquiries to make prior to PDU selection
3) Analyzing the various PDU types on the market
4) Familiarizing yourself with significant PDU attributes
5) Identifying the suitable PDU for your specific needs
How to Choose a PDU for Your Network or Data Center
These are the top 6 factors to consider in your buying decision:
1. Horizontal vs. Vertical Installation: PDUs can be mounted horizontally or vertically inside or outside the rack enclosure:
A) Horizontal PDUs are positioned within the rack and occupy either one or two rack spaces, typically ranging from 1U to 2U in size. Due to their compact dimensions, horizontal PDUs are equipped with a limited number of outlets.

B) Vertical PDUs have the flexibility to be installed either on the back or side of the rack enclosure. In instances of deep racks, there is usually sufficient room within the enclosure to accommodate vertical PDUs. These PDUs can offer a significant number of outlets, with some models featuring up to 40 outlets.

What is a 0U PDU?
A vertical PDU, also referred to as a 0U or "zero U" PDU, occupies no rack units. It attaches to the vertical posts within a rack, hence its designation as "zero U." In situations where additional space is required for IT equipment, standard 19-inch horizontal PDUs can be vertically mounted outside of the rack.
What is the most suitable PDU for a 42U rack?
A 42U rack represents the standard size for floor-standing server racks. The ideal PDU selection for such a rack depends on the number of devices intended for installation and their respective power requirements. If densely packed 1U servers will be housed in the rack, it's crucial to opt for a PDU offering sufficient outlet receptacles, along with additional open outlets for potential expansion. Vertically mounted PDUs are available with up to 48 outlets to cater to varying needs.
2. Voltage Requirements for Your Devices
Server and networking equipment in North America commonly operate on either 120V or 208/240V power systems. Conversely, Europe and Asia typically utilize 230V power sources. It's essential to ensure compatibility between the input plug of the PDU and the receptacles of your power source to avoid any mismatch.

3. Types of Outlets
Ensure that the outlets on the PDUs correspond to the plugs used by the equipment you intend to connect. Some PDUs may provide a variety of outlet types to accommodate different devices.
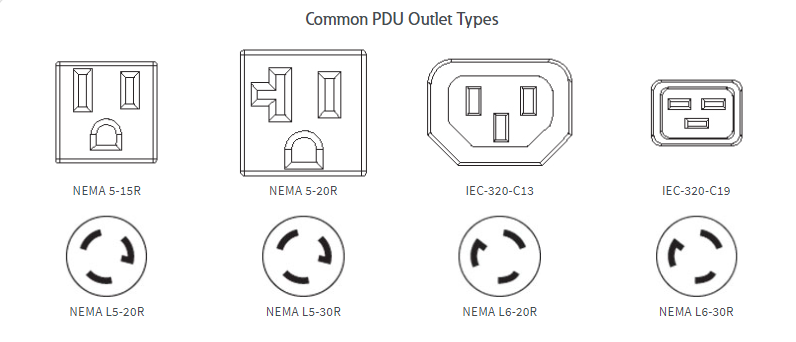
4. Outlet Quantity
opt for a PDU with a greater number of outlets than your current requirement to allow for potential expansion of your rack setup in the future.

5. Maximum Power Handling
Ensure that the combined power consumption of devices connected to the PDU does not surpass its maximum load capacity, measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA). In North America, there's typically an 80% limit on both input and output capacity (referred to as "agency de-rating"). For instance, a single-phase PDU with a nominal voltage of 120V and a de-rated input current of 12A (80% of 15A), has a load capacity of 1.44 kVA (120V x 12A).
6. Additional Functionalities
Remote management software, such as AMP's Power Alert Device Manager (PADM), empowers the remote administration of PDUs integrated with an LX network interface card. The most recent iteration, Power Alert Device Manager 20.0 (PADM20), offers customizable and user-friendly remote management features, enhanced maintenance options, and the ability to backup and restore device configurations.
Automatic device reboots are facilitated by AMP PDUs featuring an LX network interface card, which incorporate an Auto-Probe functionality. This feature autonomously identifies and resolves network connectivity issues, mitigating the need for expensive service calls for basic reboots. For instance, a PDU can be set up to conduct network pings on a router. Should the router fail to reply, the PDU will automatically reboot the router.
Environmental monitoring is facilitated by the network interface of a monitored or switched PDU, which can interface with environmental sensors linked to the PDU. These sensors oversee the surrounding temperature and humidity, along with the status of alarm, security, and telecom products via contact closures.
Selecting the optimal PDU for A/V racks hinges on the particular application and configuration. In scenarios like a conference room, which operates intermittently, lacks continuous networking needs, and powers down during idle periods, a straightforward rack mounted PDU is often sufficient.
A more intricate A/V setup, like a multi-room system, digital signage network, or control center, will encompass a greater array of components and elevated requirements. It is expected to operate continuously, necessitating remote monitoring and rebooting capabilities for devices, along with secure access measures.
Types of PDUs Available
A fundamental PDU delivers dependable distribution of AC power to numerous devices from sources such as a UPS system, generator, or utility power.
Local metered PDUs feature digital load ammeters for on-site current monitoring, assisting IT managers in load balancing and overload prevention. Some variants also offer premium Isobar surge protection.
Monitored PDUs offer the functionalities of Local Metered PDUs, along with a network interface that facilitates remote monitoring and control from virtually any location.
Switched PDUs encompass all the functionalities of Monitored PDUs, in addition to offering local or remote control over individual outlets. This allows IT administrators to avoid expensive onsite visits by remotely restarting malfunctioning devices and toggling power on and off for each outlet as needed.
A switched PDU is essential for specific IT scenarios
1. Branch offices or retail stores lacking IT personnel: Personnel managing IT equipment in remote locations can remotely control and reboot devices, avoiding the need for costly onsite visits.
2. Edge computing deployments: With edge deployments often situated far from central offices, a switched PDU's built-in intelligence allows IT managers to troubleshoot and address uptime issues from any location.
3. Remote or difficult-to-access sites: Switched PDUs enable IT personnel to perform simple reboots without physically visiting distant locations, such as cell towers, security camera spots, or ATMs.
4. Non-traditional IT environments: Switched PDUs equipped with environmental sensors can monitor temperature, humidity, and security alarm status in areas not originally designed for IT equipment, such as small closets or repurposed spaces.
An Auto Transfer Switch (ATS) PDU offers a backup power solution for network devices with single power cords. In the event of instability or failure in the primary power source, the ATS automatically switches to the secondary power source until the primary input is back to normal.
Hot-Swap PDUs are equipped with two AC inputs and a manual transfer switch, enabling seamless maintenance, repair, or replacement of compatible UPS systems without disrupting power supply to connected equipment.
Network Switch/PDU Combo Units integrate a managed or unmanaged Gigabit Ethernet switch with a network-grade PDU into a single unit. Occupying only 1U of rack space, these units are ideal for distributed networks with limited space availability. Some models also feature Power over Ethernet (PoE) functionality.
Below is a chart outlining the features and benefits of different PDUs to assist you in identifying the most suitable PDU for your requirements.
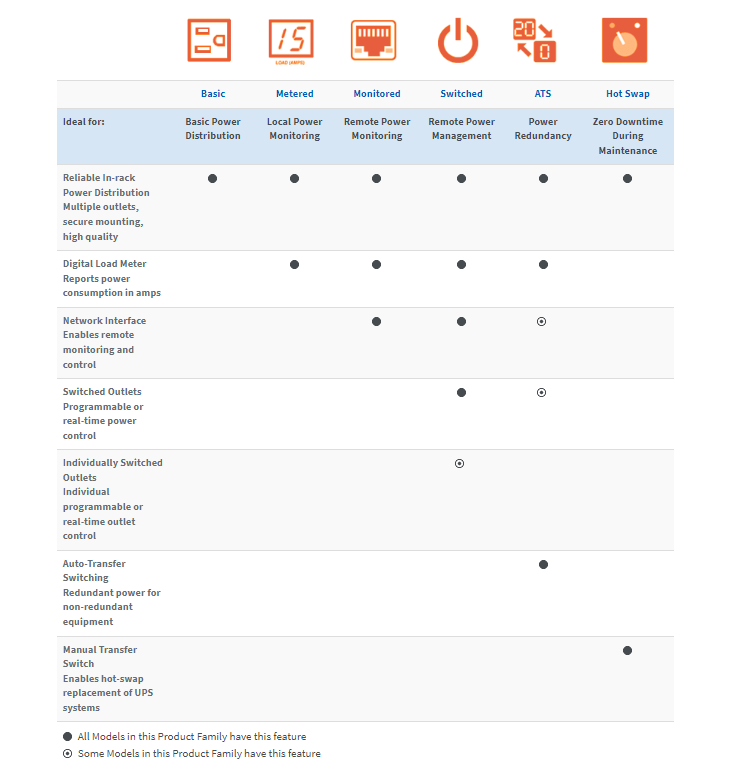
PDU Features Overview
PDUs are available in horizontal or vertical configurations. Horizontal PDUs fit within a rack, occupying 1U or 2U of space, with reversible mounting ears for front- or rear-facing installation. On the other hand, vertical PDUs mount on rack posts, taking up 0U of space and accommodating up to 48 outlets per PDU. AMP's vertical PDUs feature tool less mounting for easy installation.
Local Metered PDUs feature a digital load meter on the front panel, displaying total PDU output current for local load monitoring. Multiple load banks each have a dedicated meter, helping prevent overloads and downtime. Additionally, some PDUs include a built-in LX Platform network management card for enhanced remote monitoring capabilities. This allows for automated email notifications, monitoring of environmental sensors, and remote control of individual outlets for Switched PDUs.
Accurate power measurement features are essential for applications requiring precise electricity consumption tracking. Circuit breakers are commonly included in PDUs to safeguard against overloads and short circuits. PDUs with auto transfer switching ensure redundant power to devices without redundant power supplies, while hot-swap capability allows for maintenance or equipment replacement without interrupting power. Moreover, PDUs with automatic device reboot capability automatically detect and address network connectivity issues, reducing the need for on-site visits.
Convenience and durability features include various mounting options, detachable brackets for cord retention, and metal housing for enhanced durability. Longer cords provide flexibility in placement, while heavy-duty cords ensure reliable performance under heavy loads.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does a UPS differ from a PDU?
A UPS, or Uninterruptible Power Supply, offers battery backup during power outages, alongside power filtration and surge protection. Conversely, a Power Distribution Unit (PDU) solely distributes power from the UPS or other AC sources to multiple devices but does not generate or condition power independently.
2. What is the optimal power supply for a rack?
A PDU is tailored for powering various devices within a server rack or enclosure, ensuring efficient distribution of available amperage to maintain operational efficiency. PDUs are available in diverse styles, providing basic power distribution to advanced remote power management capabilities.
3. How does a PDU differ from a rack-mount power strip or surge protector?
While both PDUs and power strips/surge protectors offer multiple outlets, PDUs excel in robust distribution of reliable network power for various IT devices. PDUs evenly distribute available amperage among outlets, supporting higher maximum load capacities than power strips. Furthermore, PDUs may offer input current monitoring, remote control, secure access, and environmental monitoring features.
4. What sets apart a power distribution unit from a power distribution center or cabinet?
A power distribution cabinet, also referred to as a power distribution center, serves as electrical equipment for supplying and redistributing electrical energy, along with protecting power lines from overload and short circuit currents.
Utilizing a hot-swap PDU involves leveraging its dual input and manual bypass functionalities to facilitate maintenance tasks on the UPS system without disrupting the operation of connected critical equipment or requiring specialized service technicians. Here's a breakdown of the steps for using a hot-swap PDU:
1. Connect the primary input of the hot-swap PDU to an online UPS system.
2. Connect the secondary input to utility power, such as a wall outlet.
3. If maintenance, repair, or replacement of the UPS is necessary, utilize the manual transfer switch to transition the connected load to the secondary input. This action ensures continuous power supply to the equipment.
4. Upon completion of UPS maintenance, switch the PDU back to the primary input to restore the normal operation of the UPS system.
A PDU with monitoring or remote-control capabilities includes a network interface that allows it to receive data from environmental sensors linked to the PDU. This functionality aids in maintaining ideal operating conditions by monitoring factors such as ambient temperature and humidity, as well as the status of alarm, security, and telecom devices.
Check out AMP’s wide range of copper cables with all specifications and product details